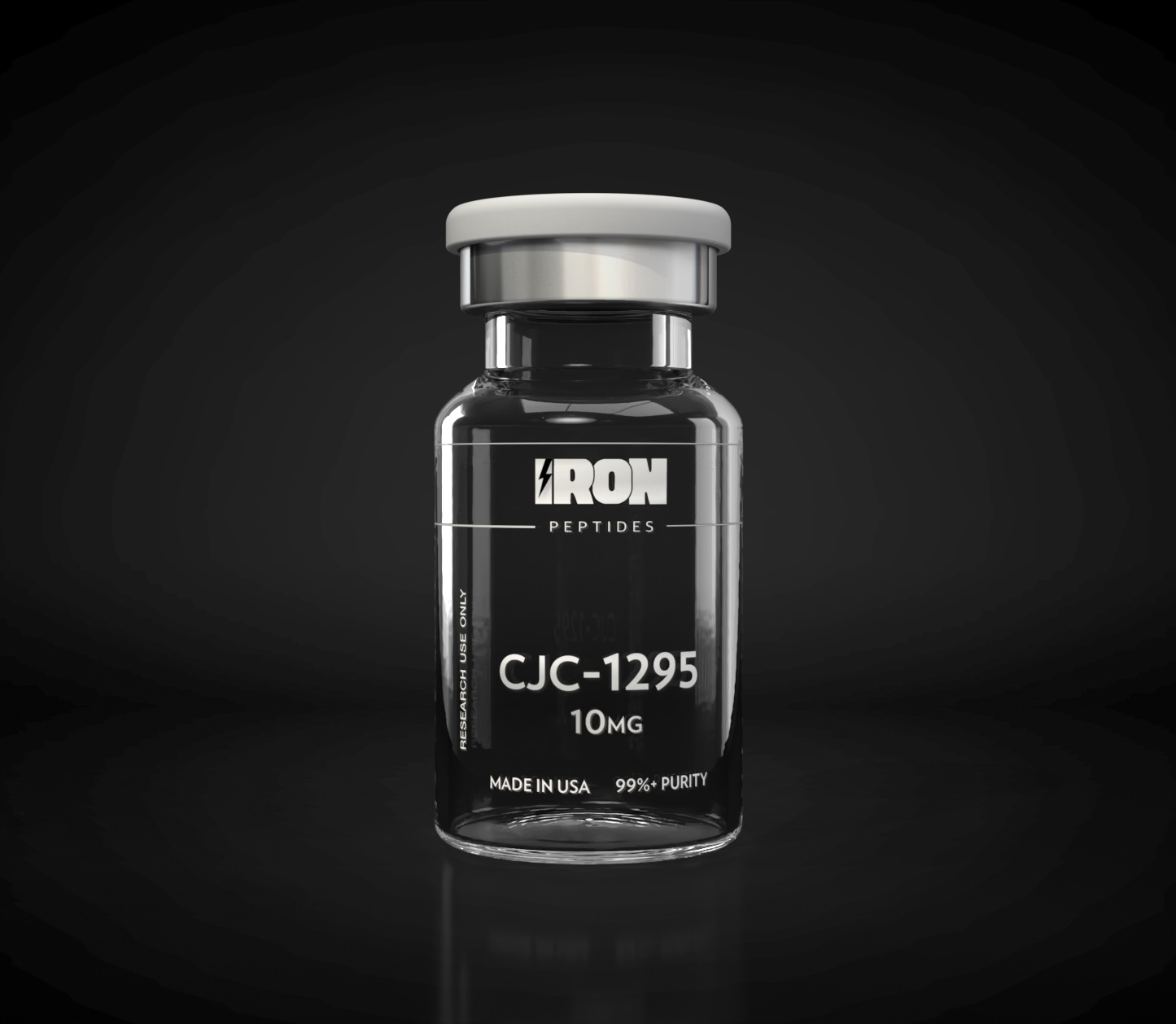
MOTS-C (10MG)
$79.99
Shipping Calculated at checkout.
Out of stock
Email when stock available
FREE SHIPPING
99%+ PURITY
MADE IN USA

What is MOTS-C (10MG)?
MOTS-c is a mitochondrial-derived peptide (MDP) currently being studied for its role in regulating metabolism, supporting healthy aging, and optimizing cellular performance. Encoded in the mitochondrial genome, MOTS-c acts as a bioactive signaling peptide, helping to manage energy balance, glucose metabolism, and exercise capacity in preclinical research.
Recent studies suggest MOTS-c may operate not just in mitochondria but throughout the body—circulating in the bloodstream and even entering the cell nucleus to support metabolic regulation and longevity pathways. Ongoing research continues to explore its potential in areas like weight management, bone density, and overall resilience, making MOTS-c a key focus in the field of regenerative and performance-based studies.

Chemical Structure of MOTS-C (10MG)
MOTS‑c consists of the 16‑amino acid sequence Met–Arg–Trp–Gln–Glu–Met–Gly–Tyr–Ile–Phe–Tyr–Pro–Arg–Lys–Leu–Arg, with a molecular formula of C₁₀₁H₁₅₂N₂₈O₂₂S₂ and a molecular weight of approximately 2,174.6 Da, as listed in PubChem (CID 255386757). Also known as the 12S rRF‑encoded mitochondrial peptide, MOTS‑c is conserved across human mitochondrial DNA [1][4][5].

What Are the Effects of MOTS-C (10MG)?
Energy and Metabolic Regulation:
MOTS‑c activates the AICAR–AMPK pathway, increasing endogenous AICAR and enhancing energy expenditure, glucose utilization, and fatty acid oxidation in rodent models [2][6].
Insulin Sensitivity:
In high-fat-fed mice, MOTS‑c improved insulin responsiveness and glucose tolerance compared to controls [4].
Muscle Endurance:
Animal studies demonstrate enhanced mitochondrial performance, endurance capacity, and physical activity when MOTS‑c is combined with exercise [3][7].
Cardiovascular Support:
By activating AMPK, MOTS‑c reduces vascular calcification and restores mitochondrial function in heart tissue [2][8].
Longevity‑Related Benefits:
Endogenous MOTS‑c decreases with age; long-term administration in aged mice enhances metabolic resilience, improves fitness, and promotes healthspan [3][5][9].
Citations
- PubChem Compound Summary for MOTS‑c (CID 255386757): sequence Met–Arg–Trp–Gln–Glu–Met–Gly–Tyr–Ile–Phe–Tyr–Pro–Arg–Lys–Leu–Arg; molecular formula C₁₀₁H₁₅₂N₂₈O₂₂S₂; MW 2,174.6 Da.
- Wan W, Zhang L, Lin Y, et al. “Mitochondria‑derived peptide MOTS‑c: effects and mechanisms related to stress, metabolism and aging.” J Transl Med. 2023;21:36.
- Lee C‑D, Kim K‑H, Cohen P. “MOTS‑c: a novel mitochondrial‑derived peptide regulating muscle and fat metabolism.” Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;100:182–369. PMID: 29969709.
- Reynolds JC, et al. “Late‑life intermittent MOTS‑c treatment reverses aging phenotypes in skeletal muscle.” Geroscience. 2021;43:1231–1241. PMID: 34493885.
- Peptides.guide – “MOTS‑c profile: mitochondrial‑derived peptide regulating stress and metabolism.”
- Lee C, Zeng J, Drew BG, et al. “The mitochondrial‑derived peptide MOTS‑c promotes metabolic homeostasis and reduces obesity and insulin resistance.” Cell Metab. 2015;21(3):443–454.
- Peptides.org – “MOTS‑c promotes endurance and mitochondrial biogenesis in rodent models.”
- Zhang L, et al. “MOTS‑c prevents vascular calcification via AMPK activation in preclinical models.” Aging Cell. 2022;21:e13605. PMID: 35145602.
- Reynolds JC, Lai RW, Woodhead JST, et al. “MOTS‑c is an exercise-induced mitochondrial-encoded regulator of age-dependent physical decline and muscle homeostasis.” Nat Commun. 2021;12:470.
 MOTS-C (10MG)
MOTS-C (10MG)
| 5 star | 0% | |
| 4 star | 0% | |
| 3 star | 0% | |
| 2 star | 0% | |
| 1 star | 0% |
Sorry, no reviews match your current selections

TrustScore 4.6
Ironpeptides
4.6
17 Reviews
I decided to try something new with…
I decided to try something new with Iron Peptides, and it has already been very beneficial. Since starting, I’ve noticed many positive effects. I feel motivated to continue, and I’m confident I’ve found the right company to trust on my personal journey—Iron Peptides.
The products
The products, services and information is exceptional

Fist time trying peptides to see what…
Fist time trying peptides to see what all the hype was about. And. I AM HOOKED! Have never felt. Better. 5 months after my neck surgery and I feel amazing. Recovery was easy and I have all my strength back!!
I decided to try something new with…
I decided to try something new with Iron Peptides, and it has already been very beneficial. Since starting, I’ve noticed many positive effects. I feel motivated to continue, and I’m confident I’ve found the right company to trust on my personal journey—Iron Peptides.
The products
The products, services and information is exceptional

Fist time trying peptides to see what…
Fist time trying peptides to see what all the hype was about. And. I AM HOOKED! Have never felt. Better. 5 months after my neck surgery and I feel amazing. Recovery was easy and I have all my strength back!!









